Page 43 - IDEA Studie 07 2023 TACR
P. 43
ARE SUBSIDIES TO BUSINESS R&D EFFECTIVE? REGRESSION
DISCONTINUITY EVIDENCE FROM THE TA CR ALFA PROGRAMME IDEA 2023
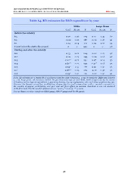
Table A4. RD estimates for R&D expenditure by year
SMEs
St. err. N
0.26 179 0.25 187 0.14 211
0 220
0.21 204 0.24 195 0.21 194 0.23 190
0.3 177 0.29 170 0.32 161
Large firms
Before the subsidy
t-3
t-2
t-1
t (year before the start o the project) During and after the subsidy t+1
t+2 t+3 t+4 t+5 t+6 t+7
Coef.
0.27 -0.02 0.04 0
0.33
0.29 0.62*** 0.60*** 0.63** 0.88*** 0.65**
Coef.
0.10 -0.30 0.09 0
-0.02 -0.09 0.07 -0.41** 0.01 -0.27 -0.02
St. err. N
0.39 87 0.28 91 0.17 94 0 98
0.23 97 0.18 97 0.19 96 0.18 95 0.32 95 0.38 95 0.36 91
Note: RD estimates for a bandwith of 5 points around the cutoff. Columns 2–4 report results for SMEs and Columns 5–7 for large firms. All estimates include the pre-treatment logs of total R&D, R&D components by the source of funding and the type of expenditure, a patenting dummy, logs of employment, sales and labour productivity, age, dummies for foreign ownership, stockholding, Prague location and co-operation with a research organisation, the number of project participants, and year and call fixed effects as controls. Standard errors are clustered at the firm level. N is the number of observations. * p<0.1, ** p<0.05, *** p<0.01.
Source: Based on micro data from CZSO (2022), ISVaV (2022) and TA CR (2017).
41